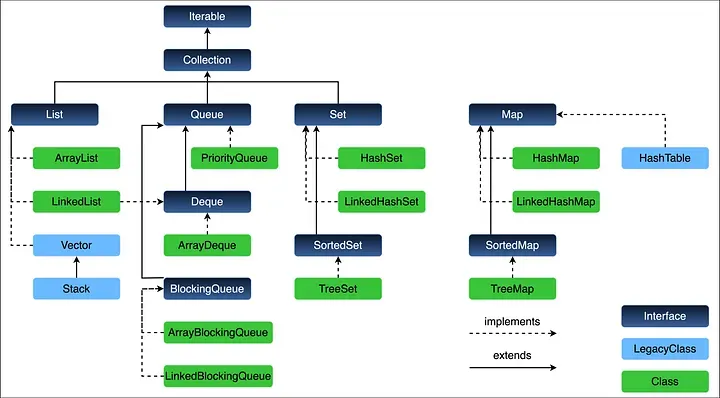
[Day15] Stack, Queue, PriorityQueue
[Day15] Stack, Queue, PriorityQueue
Stack (LIFO - Last In First Out)
Stack은 후입선출(LIFO) 구조를 가지며, 가장 나중에 들어온 요소가 먼저 제거된다.
주요 메서드
push(E e): 요소 추가pop(): 맨 위 요소 제거 및 반환peek(): 맨 위 요소 확인 (제거하지 않음)isEmpty(): 스택이 비어있는지 확인
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); // 인스턴스 생성
stack.push("첫 번째");
stack.push("두 번째");
stack.push("세 번째");
String topE = stack.pop();
System.out.println("제거된 요소: " + topE);
System.out.println("제거 후 stack: " + stack);
String peekE = stack.peek();
System.out.println("맨 위 요소: " + peekE);
System.out.println("peek 후 stack: " + stack);
boolean isEmpty = stack.isEmpty();
System.out.println("스택이 비어있나요? " + isEmpty);
}
}
Queue (FIFO - First In First Out)
Queue는 선입선출(FIFO) 구조를 가지며, 먼저 들어온 요소가 먼저 제거된다.
주요 메서드
offer(E e): 요소 추가poll(): 맨 앞 요소 제거 및 반환peek(): 맨 앞 요소 확인 (제거하지 않음)isEmpty(): 큐가 비어있는지 확인
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class LinkedListQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer("첫 번째");
q.offer("두 번째");
q.offer("세 번째");
System.out.println("현재 큐 상태 : " + q);
String e = q.poll();
System.out.println("제거된 요소 :" + e);
System.out.println("제거된 후 큐 상태 : " + q);
e = q.peek();
System.out.println("맨 앞 요소 :" + e);
System.out.println("peek 후 큐 상태 : " + q);
boolean isEmpty = q.isEmpty();
System.out.println("큐가 비어있나요? " + isEmpty);
}
}
PriorityQueue (정렬된 큐)
PriorityQueue는 내부적으로 완전 이진 트리(힙) 구조를 가지며, 기본적으로 최소 힙으로 동작한다. (가장 작은 값이 먼저 나옴)
특징
- 추가/삭제:
O(log n) - 검색:
O(n) - 기본적으로 최소 힙 (오름차순 정렬)
주요 메서드
offer(E e): 요소 추가poll(): 최우선 요소 제거 및 반환peek(): 최우선 요소 확인 (제거하지 않음)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
//정렬이 되는 Queue 생성
Queue<Integer> pq=new PriorityQueue();
//요소 추가
pq.offer(30);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [30] */
pq.offer(10);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [10, 30] */
pq.offer(20);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [10, 30, 20] */
pq.offer(50);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [10, 30, 20, 50] */
pq.offer(40);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [10, 30, 20, 50, 40] */
pq.offer(5);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [5, 30, 10, 50, 40, 20] */
pq.offer(25);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [5, 30, 10, 50, 40, 20, 25] */
pq.offer(15);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [5, 15, 10, 30, 40, 20, 25, 50] */
pq.offer(35);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [5, 15, 10, 30, 40, 20, 25, 50, 35] */
pq.offer(1);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [1, 5, 10, 30, 15, 20, 25, 50, 35, 40] */
//요소 제거
Integer min=pq.poll();
System.out.println("가장 작은 요소 : "+min); /* 1 */
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [5, 15, 10, 30, 40, 20, 25, 50, 35] */
min=pq.poll();
System.out.println("가장 작은 요소 : "+min); /* 5 */
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : "+pq); /* [10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 35, 25, 50] */
PriorityQueue를 최대 힙으로 변환
기본적으로 PriorityQueue는 최소 힙으로 동작하지만, Comparator를 이용해 최대 힙으로 변환할 수 있다.
방법
1
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
예제 코드 (최대 힙)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
import java.util.*;
public class MaxHeapPriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
pq.offer(30);
pq.offer(10);
pq.offer(20);
pq.offer(50);
pq.offer(40);
pq.offer(5);
pq.offer(25);
pq.offer(15);
pq.offer(35);
pq.offer(1);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 (최대 힙) : " + pq);
Integer max = pq.poll();
System.out.println("가장 큰 요소 : " + max);
System.out.println("현재 PQ의 상태 : " + pq);
}
}
| 자료구조 | 구조 | 특징 |
|---|---|---|
| Stack | LIFO | push(), pop(), peek(), isEmpty() |
| Queue | FIFO | offer(), poll(), peek(), isEmpty() |
| PriorityQueue | 최소 힙 기본 | offer(), poll(), peek() (추가/삭제 O(log n)) |
| Max Heap (PriorityQueue) | 최대 힙 변형 | new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()) |
STUDY
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 백준_행렬곱셈_2740 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] matrixA = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
matrixA[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
int[][] matrixB = new int[m][k];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
matrixB[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int[][] c = new int[n][k];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
for (int x = 0; x < m; x++) {
c[i][j]+=matrixA[i][x]* matrixB[x][j];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
System.out.print(c[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
END
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.