[JS] ASCII
[JS] ASCII
알고리즘 문제를 풀다가 소문자, 대문자 판별, 숫자 판별 등의 기능을 구현해야할 때 아스키코드를 자주 사용합니다.
어렵지 않은 개념이지만 자꾸만 까먹게되서 정리를 해보았습니다.
아스키코드 (ASCII Code)
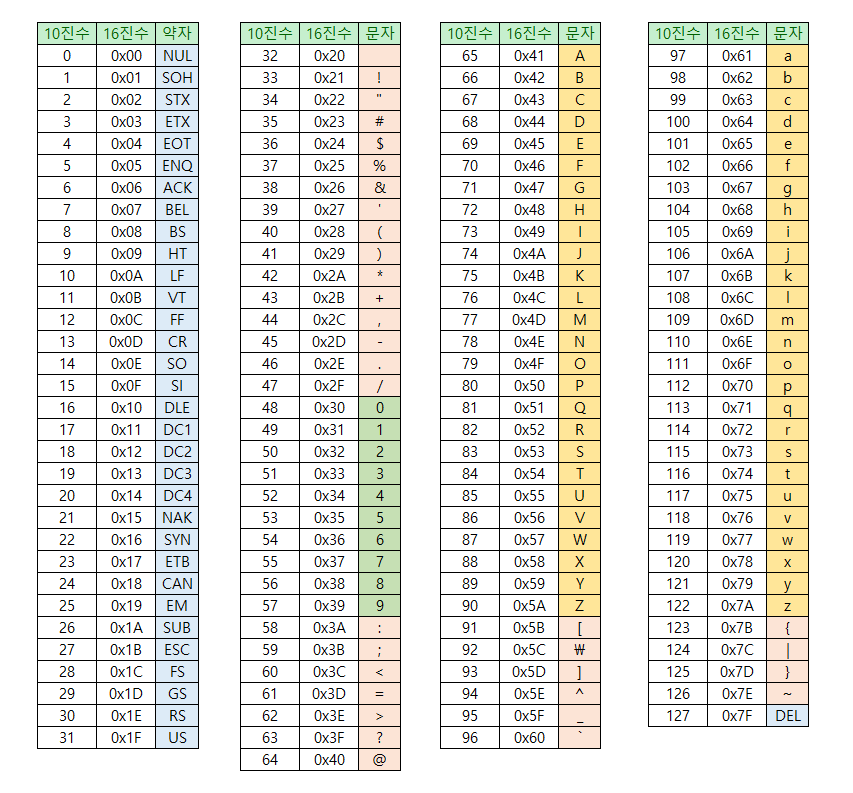
아스키코드(ASCII, American Standard Code for Information Interchange)는 문자 인코딩의 한 종류로, 컴퓨터가 문자를 저장하고 처리할 수 있도록 정수값으로 변환한 표준 코드이다.
- 7비트로 구성되며 총 128개의 문자(0~127)로 이루어져 있음
- 알파벳, 숫자, 특수문자 및 제어 문자 포함
ASCII CODE 표
| 문자 | 아스키코드 |
|---|---|
| A | 65 |
| B | 66 |
| C | 67 |
| a | 97 |
| b | 98 |
| c | 99 |
| 0 | 48 |
| 1 | 49 |
| 2 | 50 |
| ! | 33 |
| @ | 64 |
| # | 35 |
문자 -> 아스키코드
문자.charCodeAt(index)
문자열의 index 번째 문자를 아스키코드(10진수)로 변환
1
2
3
4
"h".charCodeAt(); // 104
"H".charCodeAt(); // 72
"1".charCodeAt(); // 49
" ".charCodeAt(); // 32
1
2
3
4
5
"hello".charCodeAt(0); // 104
"hello".charCodeAt(1); // 101
"hello".charCodeAt(4); // 111
"hello".charCodeAt(5); // NaN
"hello".charCodeAt(-1); // NaN
👉 문자.codePointAt(index)
유니코드 코드 포인트 값을 반환 (확장 유니코드 지원)
1
2
3
console.log("A".codePointAt(0)); // 65
console.log("a".codePointAt(0)); // 97
console.log("🔥".codePointAt(0)); // 128293 (유니코드 확장 문자도 지원)
아스키코드 -> 문자
String.fromCharCode(숫자)
아스키코드 값을 문자로 변환
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
String.fromCharCode(104); // "h"
String.fromCharCode(72); // "H"
String.fromCharCode(49); // "1"
String.fromCharCode(32); // " "
String.fromCharCode(0x68); // "h"
String.fromCharCode(0x48); // "H"
String.fromCharCode(0x31); // "1"
String.fromCharCode(0x20); // " "
👉 String.fromCodePoint(숫자)
확장 유니코드까지 변환 가능
1
2
console.log(String.fromCodePoint(128293)); // "🔥"
console.log(String.fromCodePoint(65, 66, 67)); // "ABC"
알고리즘 풀이 - 프로그래머스 Lv.2 - 시저 암호
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
function solution(s, n) {
var answer = '';
const arr = s.split("");
for(let i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++) {
if(arr[i].charCodeAt() == 32) {
answer += " ";
} else if(arr[i].charCodeAt() + n > 90 && arr[i].charCodeAt() <= 90) {
answer += String.fromCharCode(65 + ((arr[i].charCodeAt() + n) % 90) - 1);
} else if(arr[i].charCodeAt() + n > 122) {
answer += String.fromCharCode(97 + ((arr[i].charCodeAt() + n) % 122) - 1);
} else {
answer += String.fromCharCode(arr[i].charCodeAt() + n);
}
}
return answer;
}
END
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.