[Day21] MST : Minimum Spanning Tree
[Day21] MST : Minimum Spanning Tree
최소신장트리(MST, Minimum Spanning Tree)
그래프에서 모든 노드를 연결하면서 총 가중치를 최소화하는 트리
최단 경로 vs 최소신장트리
| 구분 | 최단 경로 (Shortest Path) | 최소신장트리 (MST) |
|---|---|---|
| 목적 | 특정 두 노드 간 거리를 최소화 | 모든 노드를 연결하며 최소 비용 찾기 |
| 예시 | 내비게이션 경로 찾기 | 전기 회로, 도로 건설, 통신망 구축 |
| 대표 알고리즘 | 다익스트라, 벨만-포드 | 크루스칼, 프림 |
MST 알고리즘
(1) Kruskal 알고리즘 (크루스칼)
- 간선 기반 알고리즘 → 간선의 개수가 적은 경우 유리
- 시간복잡도: (O(E \log E)) (간선 정렬이 핵심)
- 알고리즘 과정
- 모든 간선을 가중치 기준 오름차순으로 정렬
- 가장 낮은 가중치를 가진 간선부터 선택, 사이클을 형성하는 간선 제외
- (==>union()이 false이면 이미 같은 집합이므로 사이클이 있다고 간주함)
- 해당 간선을 현재의 MST(최소 비용 신장 트리)의 집합에 추가
- (V-1)개의 간선을 선택하면 종료
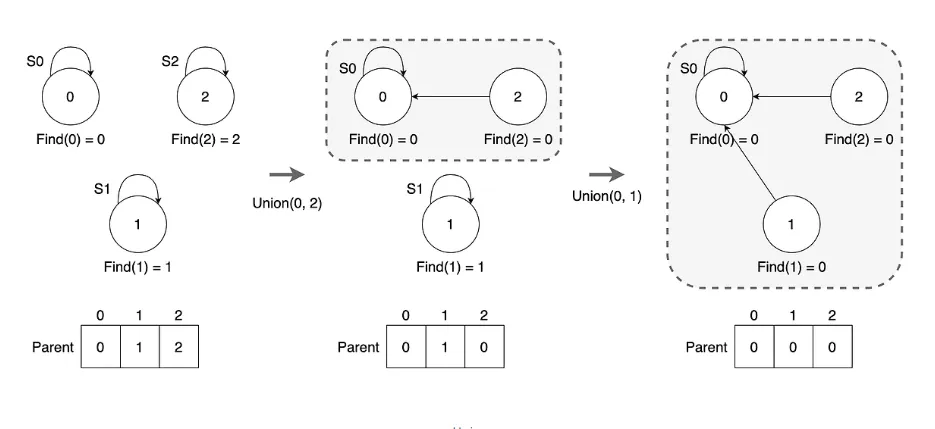
서로소 집합 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
public class DisjointSetExample {
// 부모 노드를 저장할 배열
static int[] p;
// 집합을 초기화하는 메서드
static void makeSet(int V) {
// V개의 원소를 가지는 배열을 생성
p = new int[V];
// 각 원소의 부모를 자기 자신으로 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
p[i] = i;
}
}
// 두 원소를 결합하는 메서드
static boolean union(int f, int t) {
// 각 원소의 루트 부모를 찾음
int fp = find(f);
int tp = find(t);
// 이미 같은 집합에 속하는 경우, 결합할 필요 없음
if (fp == tp) return false;
// 두 집합을 결합: t의 부모를 f의 부모로 설정
p[tp] = fp;
return true; // 결합 성공
}
// 원소의 루트 부모를 찾는 메서드
static int find(int e) {
// 경로 압축을 통해 트리의 높이를 줄임
if (e != p[e]) {
p[e] = find(p[e]); // 재귀적으로 부모를 찾음
}
return p[e]; // 최종 부모 반환
}
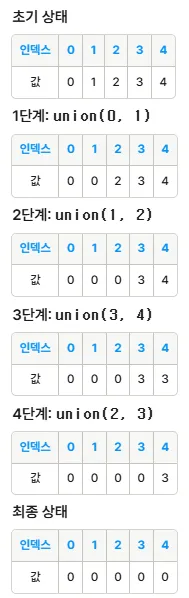
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 5개의 원소(0, 1, 2, 3, 4)로 집합을 초기화
makeSet(5);
// 원소 0과 1을 결합
union(0, 1);
// 원소 1과 2를 결합
union(1, 2);
// 원소 3과 4를 결합
union(3, 4);
// 원소 0의 루트 부모를 찾음 (0, 1, 2는 같은 집합)
System.out.println("Root of 0: " + find(0)); // 출력: Root of 0: 0
// 원소 1의 루트 부모를 찾음
System.out.println("Root of 1: " + find(1)); // 출력: Root of 1: 0
// 원소 2의 루트 부모를 찾음
System.out.println("Root of 2: " + find(2)); // 출력: Root of 2: 0
// 원소 3의 루트 부모를 찾음
System.out.println("Root of 3: " + find(3)); // 출력: Root of 3: 3
// 원소 4의 루트 부모를 찾음
System.out.println("Root of 4: " + find(4)); // 출력: Root of 4: 3
// 원소 0과 3의 루트 부모를 비교하여 서로 다른 집합인지 확인
System.out.println("Are 0 and 3 in the same set? " + (find(0) == find(3))); // 출력: false
// 원소 2와 3을 결합
union(2, 3);
// 결합 후 다시 루트 부모를 확인
System.out.println("Root of 3 after union with 2: " + find(3)); // 출력: Root of 3: 0
System.out.println("Are 0 and 3 in the same set now? " + (find(0) == find(3))); // 출력: true
}
}
Kruscal 코드 예제 (모든 정점 연결하는 최소 비용)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
/*
Q. 모든 정점을 연결하는 최소 비용을 구하라(ex.모든 도시를 여행하는 최소 비용을 구하라)
첫째줄:정점 개수
둘째줄:간선 개수
나머지:간선 정보
7
11
0 1 32
0 2 31
0 5 60
0 6 51
1 2 21
2 4 46
2 6 25
3 4 34
3 5 18
4 5 40
4 6 51
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class A076_크루스칼 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(100);
int V=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine().trim());
int E=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine().trim());
Edge []arr=new Edge[E];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
String []ftw=br.readLine().split(" ");
int from=Integer.parseInt(ftw[0]);
int to=Integer.parseInt(ftw[1]);
int weight=Integer.parseInt(ftw[2]);
arr[i]=new Edge(from, to, weight); //(2)
}
Arrays.sort(arr);// (3)
makeSet(V); // (4)
int result=0; //(5)
int pickCnt=0; //(6)
for(Edge e:arr) { //(7)
if(union(e.f,e.t)) {
result+=e.w;
if(++pickCnt==(V-1))break;
}
}
sb.append(result);
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
static boolean union(int f,int t) {
int fp=find(f);
int tp=find(t);
if(fp==tp) return false;
p[tp]=fp;
return true;
}
static int find(int e) {
if(e!=p[e]) p[e]=find(p[e]);
return p[e];
}
static int[]p;
static void makeSet(int V) {
p=new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
p[i]=i;
}
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{ //(1)
int f,t,w;
public Edge(int f, int t, int w) {
super();
this.f = f;
this.t = t;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Edge [f=" + f + ", t=" + t + ", w=" + w + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Integer.compare(w, o.w);
}
}
}
(2) Prim 알고리즘 (프림)
- 정점 기반 알고리즘 → 간선이 많을 때 유리
- 시간복잡도: (O(E \log V)) (우선순위 큐 사용)
우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)를 활용한 최소 간선 선택
- 알고리즘 과정
- 시작 단계에서는 시작 정점만이 MST(최소 비용 신장 트리) 집합에 포함된다.
- 앞 단계에서 만들어진 MST 집합에 인접한 정점들 중에서 최소 간선(PriorityQueue이용하면 쉬움)으로 연결된 정점을 선택하여 트리를 확장한다.즉, 가장 낮은 가중치를 먼저 선택한다.
- 모든 정점이 선택되었으면 끝냄.
Prim 코드 예제 (모든 정점 연결하는 최소 비용)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
/*
Q. 모든 정점을 연결하는 최소 비용을 구하라(ex.모든 도시를 여행하는 최소 비용을 구하라)
첫째줄:정점 개수
둘째줄:간선 개수
나머지:간선 정보
7
11
0 1 32
0 2 31
0 5 60
0 6 51
1 2 21
2 4 46
2 6 25
3 4 34
3 5 18
4 5 40
4 6 51
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Prim {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//System.setIn(new FileInputStream("src/jes/프림.txt"));
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(100);
int V=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine().trim());
int E=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine().trim());
int [][]arr=new int[V][V]; //(1)
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
String []ftw=br.readLine().split(" ");
int from=Integer.parseInt(ftw[0]);
int to=Integer.parseInt(ftw[1]);
int weight=Integer.parseInt(ftw[2]);
arr[from][to]=arr[to][from]=weight;
}
boolean []visited=new boolean[V];//(2)
int result=0;//(3)
int pickCnt=0;//(4)
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq=new PriorityQueue<>();//(5)
//처리
pq.offer(new Edge(0,0,0)); //1
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {//2
Edge e=pq.poll();//2-1
if(visited[e.t]) continue;//2-2
visited[e.t]=true;//2-3
result+=e.w;//2-4
if(++pickCnt==V) break;//2-5
for (int nt = 0; nt < V; nt++) {//2-6
if(!visited[nt] && arr[e.t][nt]!=0 ) pq.offer(new Edge(e.t,nt,arr[e.t][nt]));//2-6-1
}
}
sb.append(result);
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{ //(6)
int f,t,w;
public Edge(int f, int t, int w) {
super();
this.f = f;
this.t = t;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Edge [f=" + f + ", t=" + t + ", w=" + w + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Integer.compare(w, o.w);
}
}
}
Kruskal vs Prim 선택 기준
| 알고리즘 | 크루스칼 (Kruskal) | 프림 (Prim) |
|---|---|---|
| 기준 | 간선 중심 | 정점 중심 |
| 정렬 필요 여부 | O(E log E) → 간선 정렬 필요 | O(E log V) → 우선순위 큐 활용 |
| 유리한 경우 | 간선이 적을 때 (E ≈ V) | 간선이 많을 때 (E ≈ V²) |
Summary (간적쿠간만프)
- 간선이 적으면 → Kruskal (정렬 후 선택)
- 간선이 많으면 → Prim (우선순위 큐 사용)
다익스트라 알고리즘
- 가중치가 있는 그래프에서 한 정점에서 다른 정점까지의 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘
대표적인 그리디(탐욕) 알고리즘으로, 매번 가장 짧은 거리를 선택하며 진행
- 다익스트라 동작 과정
- 시작 정점으로부터의 거리를 초기화. 시작 정점의 거리는 0으로 설정하고, 나머지 정점의 거리는 무한대로 설정
- 방문하지 않은 정점 중에서 가장 짧은 거리를 가진 정점을 선택(PriorityQueue를 이용하면 쉬움)
- 선택한 정점과 연결된 인접 정점들의 거리를 업데이트. 즉, 선택한 정점을 거쳐 가는 경로가 더 짧다면 그 거리로 갱신한다는 것. 이 과정을 모든 정점이 방문될 때까지 반복.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
/*
Q.시작점에서 도착점까지의 최소비용 구하기(ex.서울에서 부산까지의 최소 톨게이트 비용은?)
첫째줄: 정점수
둘째줄: 시작정점 도착점
세째줄: 간선수
7
0 4
11
0 1 32
0 2 31
0 5 60
0 6 51
1 2 21
2 4 46
2 6 25
3 4 34
3 5 18
4 5 40
4 6 51
*/
// 엑셀 그림 참조
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Dijkstra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt(); // 정점 수
int start = sc.nextInt(); // 시작점
int end = sc.nextInt(); // 도착점
int E = sc.nextInt(); // 간선 수
int[][] arr = new int[V][V];// (1)
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int f = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
int w = sc.nextInt();
arr[f][t] = arr[t][f] = w; // 무방향 그래프인 경우
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];// (2)
int[] minDistance = new int[V];// (3)
int[] previous = new int[V]; // 경로 추적을 위한 배열
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
minDistance[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// (4)
previous[i] = -1; // 초기화
}
// int result=0;//(3)
// int pickCnt=0;//(4)
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();// (5)
// 처리
pq.offer(new Edge(start, start, 0)); // 1
minDistance[start] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {// 2
Edge e = pq.poll();// 2-1
if (visited[e.t])
continue;// 2-2
visited[e.t] = true;// 2-3
// result+=e.w;//2-4
if (e.t == end)
break;// 2-5
for (int nt = 0; nt < V; ++nt) {// 2-6
//나를통해너에게까지가는새비용=e.w+arr[e.t][i];
//누군가를통해너에게까지가는기존비용=minDistance[i];
if (!visited[nt] && arr[e.t][nt] != 0 && minDistance[nt] > (e.w + arr[e.t][nt])// 2-6-1
) {
//기존비용을 새비용으로 덮어쓴다
minDistance[nt] = (e.w + arr[e.t][nt]);// 2-6-1-1
pq.offer(new Edge(e.t, nt, minDistance[nt]));// 2-6-1-2
previous[nt] = e.t; // 이전 정점 기록
}
}
}
System.out.println(minDistance[end]);
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
for (int at = end; at != -1; at = previous[at]) {
path.add(at);
}
java.util.Collections.reverse(path); // 경로를 역순으로 저장
System.out.println("최단 경로: " + path);
sc.close();
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { // (6)
int f, t, w;
public Edge(int f, int t, int w) {
super();
this.f = f;
this.t = t;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Edge [f=" + f + ", t=" + t + ", w=" + w + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Integer.compare(w, o.w);
}
}
}
TEAM STUDY
✅ 첫번째 문제 
출력값 5.65 (X) -> 7.02 (O)
우주 정거장_Kruskal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
package algorithmTeam;
import java.util.*;
public class 우주정거장 {
static int[] parent, rank;
public static int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public static void union(int a, int b) {
int rootA = find(a);
int rootB = find(b);
if (rootA != rootB) {
if (rank[rootA] > rank[rootB]) {
parent[rootB] = rootA;
} else if (rank[rootA] < rank[rootB]) {
parent[rootA] = rootB;
} else {
parent[rootB] = rootA;
rank[rootA]++;
}
}
}
public static double kruskal(int n, int[][] planets) {
List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();
// 모든 행성 간의 거리 계산 후 간선 리스트에 추가
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(planets[i][0] - planets[j][0], 2) +
Math.pow(planets[i][1] - planets[j][1], 2));
edges.add(new Edge(i, j, distance));
}
}
Collections.sort(edges);
// 유니온-파인드 초기화
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
double mstCost = 0;
int mstEdges = 0;
for (Edge edge : edges) {
if (find(edge.u) != find(edge.v)) {
union(edge.u, edge.v);
mstCost += edge.weight;
mstEdges++;
if (mstEdges == n - 1) break;
}
}
return Math.round(mstCost * 100.0) / 100.0; // 소수점 둘째 자리 반올림
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] planets = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
planets[i][0] = sc.nextInt();
planets[i][1] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(kruskal(n, planets));
sc.close();
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int u, v;
double weight;
public Edge(int u, int v, double weight) {
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge other) {
return Double.compare(this.weight, other.weight);
}
}
}
우주 정거장_Prim
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
package algorithmTeam;
import java.util.*;
public class 우주정거장_prim {
public static double prim(int n, int[][] planets) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(new Node(0, 0)); // 시작 정점
double mstCost = 0;
int mstEdges = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node node = pq.poll();
int u = node.index;
if (visited[u]) continue;
visited[u] = true;
mstCost += node.cost;
mstEdges++;
if (mstEdges == n) break; // MST 완성
// 현재 노드와 연결될 수 있는 모든 노드 추가
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (!visited[v]) {
double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(planets[u][0] - planets[v][0], 2) +
Math.pow(planets[u][1] - planets[v][1], 2));
pq.add(new Node(v, distance));
}
}
}
return Math.round(mstCost * 100.0) / 100.0; // 소수점 둘째 자리 반올림
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] planets = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
planets[i][0] = sc.nextInt();
planets[i][1] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(prim(n, planets));
sc.close();
}
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int index;
double cost;
public Node(int index, double cost) {
this.index = index;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node other) {
return Double.compare(this.cost, other.cost);
}
}
}
✅ 두번째 문제
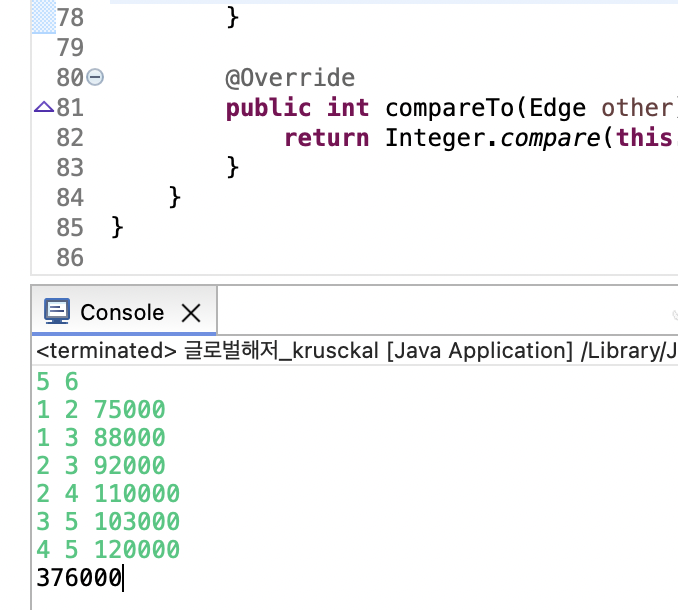
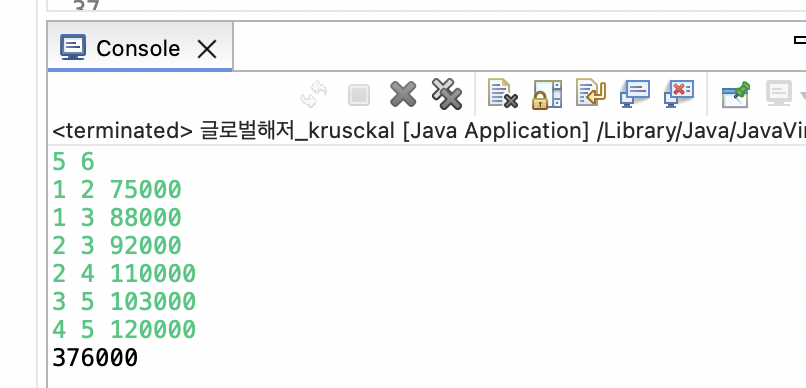
글로벌해저_Krusckal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
package algorithmTeam;
import java.util.*;
public class 글로벌해저_krusckal {
static int[] parent, rank;
public static int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public static void union(int a, int b) {
int rootA = find(a);
int rootB = find(b);
if (rootA != rootB) {
if (rank[rootA] > rank[rootB]) {
parent[rootB] = rootA;
} else if (rank[rootA] < rank[rootB]) {
parent[rootA] = rootB;
} else {
parent[rootB] = rootA;
rank[rootA]++;
}
}
}
public static int kruskal(int n, List<Edge> edges) {
Collections.sort(edges);
parent = new int[n + 1];
rank = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
int mstCost = 0, mstEdges = 0;
for (Edge edge : edges) {
if (find(edge.u) != find(edge.v)) {
union(edge.u, edge.v);
mstCost += edge.cost;
mstEdges++;
if (mstEdges == n - 1) break;
}
}
return mstCost;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
edges.add(new Edge(a, b, c));
}
System.out.println(kruskal(n, edges));
sc.close();
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int u, v, cost;
public Edge(int u, int v, int cost) {
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge other) {
return Integer.compare(this.cost, other.cost);
}
}
}
글로벌해저_Prim
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
package algorithmTeam;
import java.util.*;
public class 글로벌해저_prim {
public static int prim(int n, List<List<Node>> graph) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(new Node(1, 0));
int mstCost = 0, mstEdges = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node node = pq.poll();
int u = node.index;
if (visited[u]) continue;
visited[u] = true;
mstCost += node.cost;
mstEdges++;
if (mstEdges == n) break; // MST 완성
for (Node neighbor : graph.get(u)) {
if (!visited[neighbor.index]) {
pq.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
return mstCost;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Node(b, c));
graph.get(b).add(new Node(a, c));
}
System.out.println(prim(n, graph));
sc.close();
}
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int index, cost;
public Node(int index, int cost) {
this.index = index;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node other) {
return Integer.compare(this.cost, other.cost);
}
}
}
✅ 다익스트라 문제로 바꾸기
우주 정거장 건설 우주 탐사선들이 정거장을 세우기 위해 N개의 행성에 기지를 건설하려 한다. 각 행성은 (x, y) 좌표를 가지며, 두 행성을 연결하는 비용은 유클리드 거리로 정의된다. 첫번째 행성에서 각 행성으로 가는 최소 비용을 구하라.
글로벌 해저 케이블 네트워크 구축 한 글로벌 통신 회사가 N개의 대륙(정점)을 연결하는 M개의 해저 광케이블(간선) 후보를 조사했다. 각 해저 케이블은 특정 두 대륙을 연결하며, 설치 비용이 다르다. 시작 대륙에서 각각의 다른 대륙까지 가는 최소 비용을 구하라.
END
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.